Currently Empty: ₹0.00
Communication and Collaboration
Microsoft Defender for Office 365
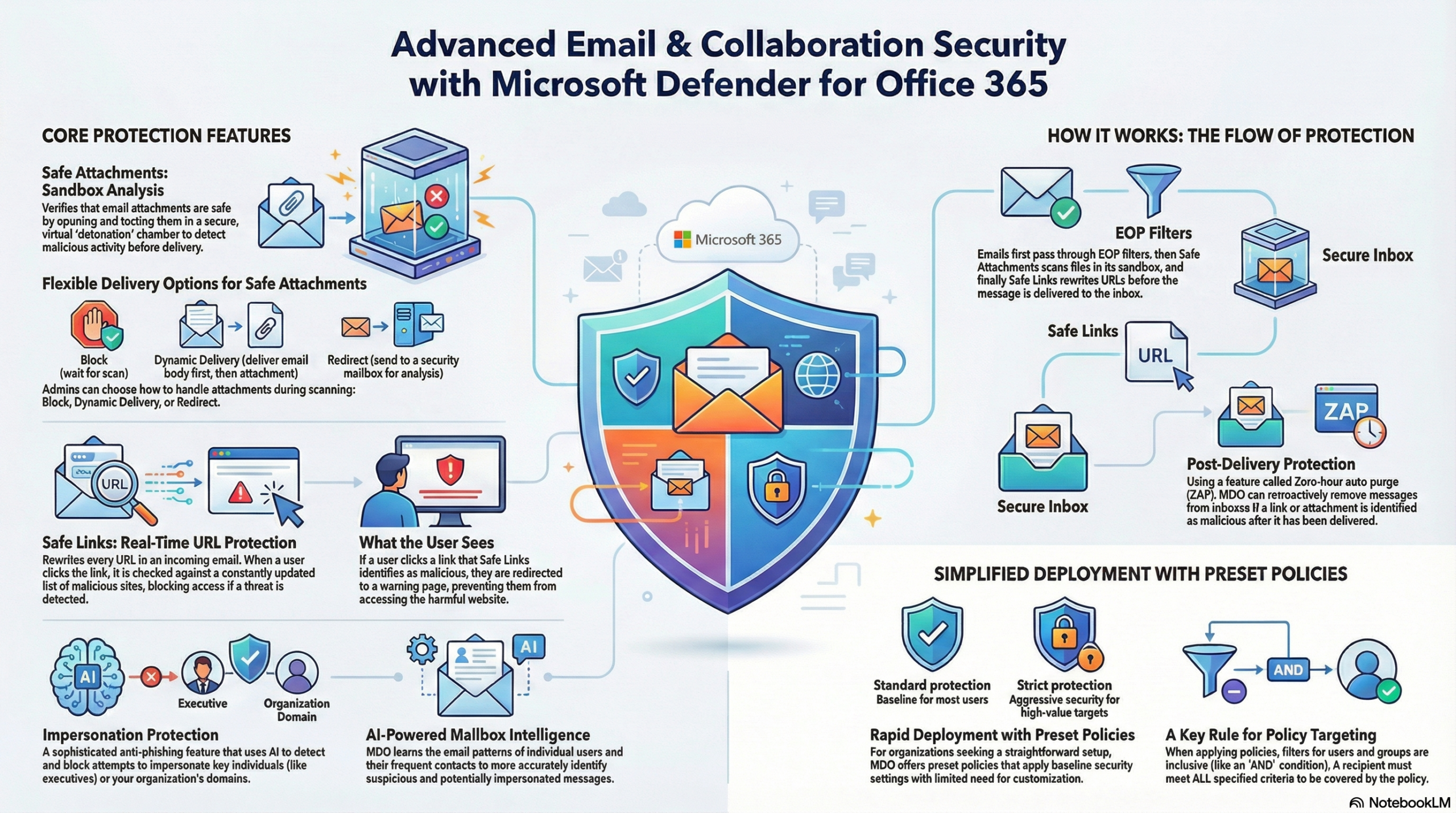
This quick learner focuses on Microsoft Defender for Office 365 (MDO). MDO provides protection against advanced threats like zero-day malware and sophisticated phishing attacks using features like sandboxing and time-of-click verification. It extends protection beyond email into Microsoft Teams, SharePoint, and OneDrive.
Microsoft Defender for Office 365 protects content across:
- Exchange Online – Email and calendar items
- Microsoft Teams – Chats, channels, and shared files
- SharePoint Online – Documents and sites
- OneDrive for Business – User file storage
This ensures end-to-end protection wherever users communicate or share files.
Licensing and Plans
Microsoft Defender for Office 365 is available in:
- Plan 1 – Core protection (Safe Links, Safe Attachments, anti-phishing)
- Plan 2 – Advanced hunting, Threat Explorer, AIR, and attack simulation
- Included with Microsoft 365 E5
Understand which tools are available based on your subscription.
| Feature Category | Default (EOP) | MDO Plan 1 | MDO Plan 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Prevent known volume-based attacks | Protect against zero-day malware & phishing | Investigation, Response & Automation |
| Protection | Anti-malware, Anti-spam, Spoofing | Safe Attachments & Safe Links | All Plan 1 features |
| Investigation | Message Trace, Audit Log | Real-time Detections | Threat Explorer (Deep search) |
| Response | ZAP, Admin Submissions | Soft-delete, Preview | Automated Investigation & Response (AIR) |
| Training | N/A | N/A | Attack Simulation Training |
1. Microsoft Defender for Office 365 Architecture
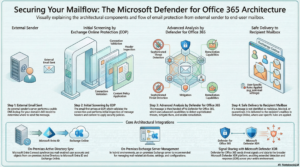
- The sender’s server looks up the MX record to route email to Exchange Online or an SMTP gateway.
- Exchange Online Protection validates the connection and scans the email. EOP validates the email with features like Connection Filtering, Anti-Malware scan, Anti-Spam Engine and Content filtering.
- Microsoft Defender for Office 365 provides advanced threat protection. MDO validates the emails with its capabilities like Anti-Phishing, User Impersonation, Domain Impersonation, Safe Link and Safe Attachment
- Safe emails are delivered to Exchange Online, where user rules and junk settings apply.
- Microsoft Entra Connect syncs on-premises Active Directory objects to Exchange Online.
- An on-premises Exchange server is recommended for supported mail attribute management.
- Defender for Office 365 shares threat signals with Microsoft Defender XDR.
2. Core Features of MDO
MDO adds three primary layers of protection that EOP does not offer:
Safe Links: Provides time-of-click verification. It scans URLs in emails, Teams messages, and Office documents. If a link is malicious, the user is blocked from accessing it.
- Key mechanism: It often rewrites URLs (e.g.,
https://nam01.safelinks.protection.outlook.com...) to proxy the traffic through Microsoft for scanning at the exact moment the user clicks, protecting against links that become malicious after delivery.
Safe Attachments: Protects against unknown malware (zero-day) by using a virtual environment (sandbox).
- Key mechanism: Detonation. Attachments are opened in a safe cloud environment to observe their behavior (e.g., registry changes, network calls) before being delivered to the user.
Impersonation Protection: Part of Anti-Phishing policies, this detects when a sender is trying to look like a high-value target (like a CEO) or a specific domain to trick users.
3. Deployment Strategy: Preset vs. Custom
You have two primary ways to deploy these protections:
A. Preset Security Policies (Recommended for ease)
Microsoft maintains these policies, meaning you cannot change individual settings within them.
- Standard Protection: Suitable for most users.
- Strict Protection: More aggressive protection (lower tolerance for false positives) suitable for high-value targets (HVTs) like executives.
- Note: You apply these to specific Users, Groups, or Domains.
B. Custom Policies (Recommended for control)
If you need granular control (e.g., specific exclusions or actions), you create custom policies in the Microsoft 365 Defender Portal -> Email & Collaboration -> Policies & Rules -> Threat Policies.
Policy Order of Precedence
When a user is targeted by multiple policies, they are applied in this strict order. Once a policy is applied, processing stops for that feature.
- Strict Preset Security Policy.
- Standard Preset Security Policy.
- Custom Threat Policies (Evaluated by priority value 0, 1, 2…).
- Default Threat Policies (or Built-in Protection).
Note: If you create a custom policy but the user is also in the “Standard” preset, the Standard preset wins and the custom policy is ignored.
4. Key Configuration Tasks
Configuring Safe Attachments
- Dynamic Delivery: This is a crucial user experience setting. It delivers the email body immediately while the attachment is being scanned in the sandbox. Once safe, the attachment is re-attached to the email.
- Quarantine Policy: Ensure this is set to AdminOnlyAccessPolicy so users cannot release malware-infected attachments themselves.
- Safe Documents: A global setting that protects users when they open files in Protected View.
Configuring Safe Links
- Internal Scanning: Ensure “Apply Safe Links to email messages sent within the organization” is checked.
- Click Tracking: Enable “Track user clicks” to audit who clicked malicious links.
- Do Not Let Users Click Through: Disable the setting “Let users click through to the original URL” to enforce the block.
Configuring Impersonation Protection
- Users to Protect: Manually add your C-suite or sensitive roles here.
- Mailbox Intelligence: Enable this. It uses AI to learn user communication patterns (who they normally email) to better distinguish between a spoofing attempt and a legitimate personal email address.
5. How It All Works Together (The Stack)
Understanding the order of processing helps with troubleshooting:
- Edge Protection: Network throttling and IP reputation (EOP).
- Sender Intelligence: Authentication (DMARC/SPF) and Spoof detection.
- Content Filtering: Safe Attachments (detonation) and Safe Links (URL reputation).
- Post-Delivery Protection: Zero-hour Auto Purge (ZAP) removes malicious emails from inboxes if they turn bad after delivery.
6. Deployment Checklist
Follow these steps to “unleash the full protection capabilities”.
- Configure Email Authentication:
- Set up SPF, DKIM, and DMARC for all custom domains.
- If using third-party gateways, configure ARC (Authenticated Received Chain).
- Enable Threat Policies:
- Recommendation: Start with Standard Preset Security Policies for all users unless a specific business need requires custom settings.
- Use Strict Preset Policies for high-value targets (executives).
- Assign Permissions:
- Use the Security Administrator role for team members managing MDO to follow least-privilege principles (avoid using Global Admin).
- Configure Reporting:
- Deploy the Report Message button in Outlook so users can report false positives/negatives.
- Decide if reports go to Microsoft, a custom mailbox, or both.
- Set Up Priority Accounts:
- Tag up to 250 high-value users (Plan 2) to give them additional heuristics and visibility.
7. Key Terminology
- AIR (Automated Investigation and Response): A Plan 2 feature that automatically investigates compromised users and emails.
- Dynamic Delivery: A Safe Attachments feature where the email body is delivered immediately while the attachment is scanned/detonated.
- Tenant Allow/Block List: The central location to override verdicts for URLs, files, and senders. Blocks are preferred over allows.
- Configuration Analyzer: A tool to compare your current custom policy settings against the recommended Standard/Strict baselines.
8. Threats Addressed
Defender for Office 365 is designed to mitigate:
- Phishing and Spear-Phishing attacks
- Business Email Compromise (BEC)
- Malware and Ransomware
- Zero-day threats
- Malicious URLs and attachments
- Impersonation and spoofing attacks
9. Core Components and Features
9.1 Anti-Phishing Protection
Anti-phishing uses machine learning models to analyze:
- Sender reputation and domain authenticity
- Message content, structure, and intent
- User behavior patterns
It also provides:
- Impersonation protection for executives and high-risk users
- Spoof intelligence to detect forged sender addresses
9.2 Safe Links
Safe Links protects users from malicious URLs by:
- Scanning links in emails, Office documents, and Teams messages
- Performing time-of-click verification, even after delivery
- Blocking access to compromised or newly weaponized websites
This ensures that links are checked at the moment the user clicks them, not just when the email arrives.
9.3 Safe Attachments
Safe Attachments uses a secure sandboxing environment to:
- Detonate email attachments and files
- Observe behavior such as file execution, registry changes, and network calls
- Block files exhibiting malicious behavior
It protects against zero-day malware that traditional antivirus solutions may miss.
9.4 Threat Explorer (Real-timee-time Detections)
Threat Explorer provides administrators with:
- Detailed views of detected threats
- Email timelines and attack paths
- Advanced filtering and search capabilities
This helps security teams quickly identify affected users and take corrective actions.
9.5 Automated Investigation and Response (AIR)
AIR reduces manual workload by:
- Automatically investigating alerts
- Identifying root causes
- Remediating threats by quarantining emails or blocking URLs
It ensures faster response times and consistent security actions.
10. Best Practices
- Enable Safe Links and Safe Attachments for all users
- Configure impersonation protection for executives
- Regularly review Threat Explorer and reports
- Run attack simulation training to improve user awareness
- Keep security policies aligned with organizational risk levels