This lesson is on Active Directory Fundamentals, covering key concepts, components, and terminology.
1. Modern Identity
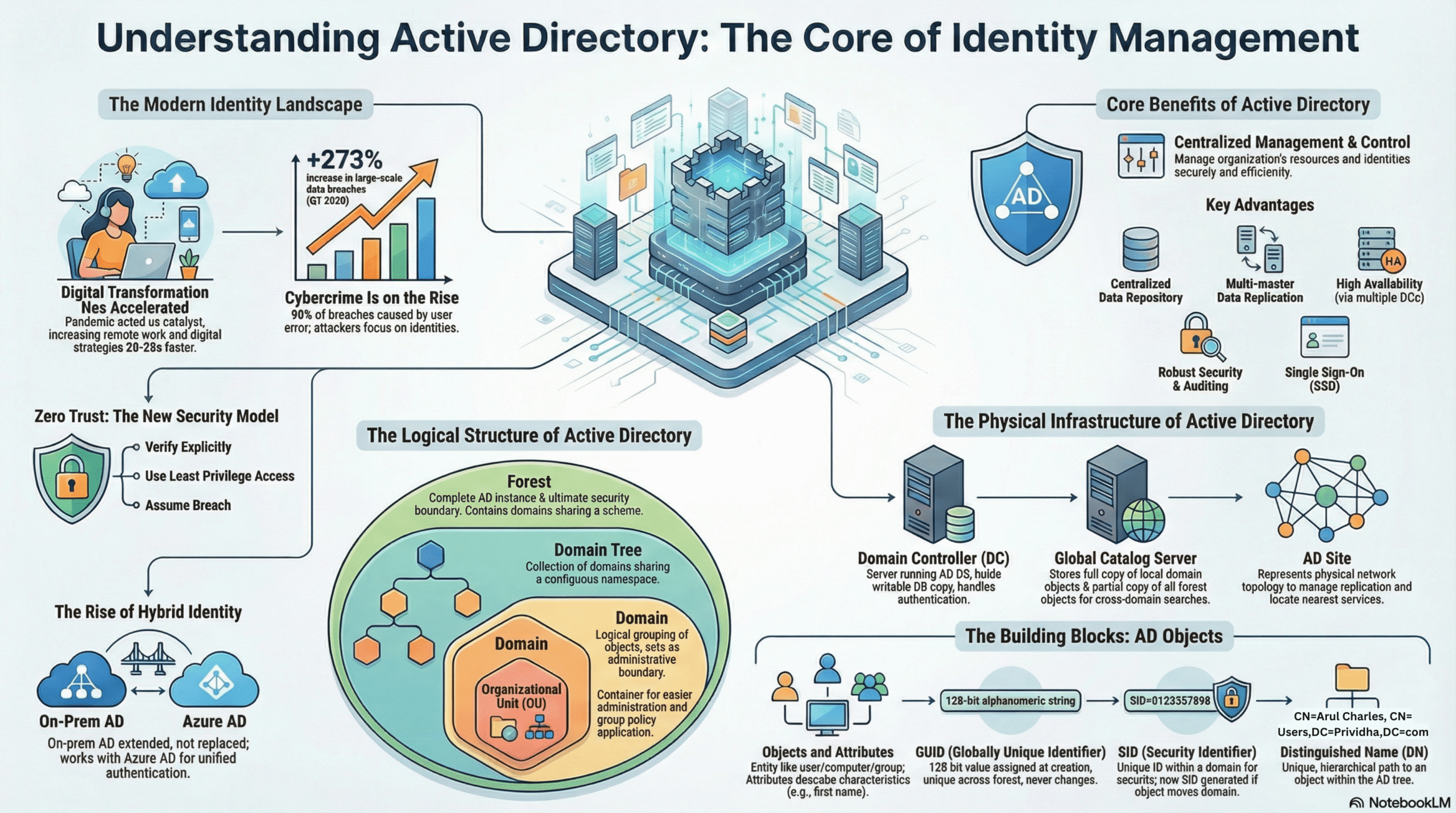
Active Directory (AD) is a directory service by Microsoft that helps organizations manage users, computers, and resources in a centralized way. It provides authentication, authorization, and policy enforcement, allowing administrators to control access and security across a network.
Identity as Perimeter: The traditional network perimeter defense model is obsolete due to remote work and cloud adoption. Identity is the new security perimeter.
Zero Trust Security: A security model essential for modern AD environments, based on three principles:
- Verify Explicitly: Always authenticate and authorize based on all available data points.
- Least Privilege Access: Limit user access with Just-In-Time and Just-Enough-Administration (JEA).
- Assume Breach: Minimize blast radius and segment access.
The Rise of Cybercrime: Attackers (like those in the Nobelium/SolarWinds attack) target on-premises AD to move laterally and forge tokens (e.g., SAML) to access cloud resources.
2. Active Directory vs. Entra ID (Azure Active Directory)
These are distinct solutions that work together in a Hybrid Identity model.
| Feature |
Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) |
Entra ID (Previously Azure Active Directory) |
| Primary Role |
On-premises directory service managing legacy apps and devices. |
Cloud-based Identity as a Service (IDaaS) for SaaS and web apps. |
| Authentication |
Kerberos, NTLM, LDAP. |
SAML, OAuth2, WS-*, OpenID Connect. |
| Device Mgmt |
Group Policy Objects (GPOs). |
Microsoft Endpoint Manager (Intune). |
| Management |
It is hierarchical, Manual management of OUs, groups, and trusts. |
Flat structure; uses dynamic groups and Conditional Access. |
3. Logical Components (Structure)
Logical components define the organization of resources and are independent of physical location.
Forest: The highest logical container. It represents a complete AD instance and is the security boundary. All domains in a forest share a common schema and configuration.
Domain: A logical partition used for authentication, replication, and policy scope. It shares a common database within the forest but has its own unique policies and administrator limits.
Domain Tree: A collection of domains sharing a contiguous namespace (e.g., Prividha.com and Marketting.Prividha.com).
Organizational Unit (OU): A container within a domain used to group objects (users, computers) for the purpose of applying Group Policies or Delegating Control.
4. Physical Components (Infrastructure)
Physical components control replication and traffic flow.
Domain Controller (DC): A server hosting the AD DS role and a copy of the directory database (ntds.dit).
Global Catalog (GC): A DC that holds a full writable copy of its own domain’s objects and a partial, read-only copy of every object in the forest. It is essential for universal group membership queries and logins.
AD Sites: Logical representations of physical network segments (subnets). Sites are used to control replication traffic (schedule/frequency) and ensure clients authenticate with the nearest DC (Service Location).
5. Key Object Identifiers
Every object in AD is tracked using unique identifiers.
GUID (Globally Unique Identifier): A 128-bit value stored in the objectGUID attribute. It is immutable; it never changes, even if the object is moved to a different domain.
SID (Security Identifier): stored in the objectSid attribute. It is unique within a domain. If a user moves to a new domain, they get a new SID, and the old SID is stored in sIDHistory to maintain access to resources,.
Distinguished Name (DN): The full path to an object (e.g., CN=John Samuel,CN=Users,DC=Prividha,DC=com). This changes if the object is moved to a different OU.
6. Core Benefits of Active Directory
Centralized Repository: Stores identity data in the ntds.dit file based on the JET database engine.
Replication: Uses multi-master replication, allowing changes to occur on any DC (except for FSMO roles).
High Availability: Built-in fault tolerance via multiple domain controllers.
Single Sign-On (SSO): Enables users to authenticate once to access multiple integrated applications.